CHEMISTRY SOLUTION
1A
A transmission element is a component that transfers data or energy from one point to another.
1bi. Element D-288 forms a doubly charged cation.
1bii. The soluble trioxocarbonate (IV) is CO32-.
1C.
The general decrease in the first ionization energies of the period in the periodic table is due to the increase in atomic radius and the decrease in effective nuclear charge.
1d.
-methane (CH4)
-propane (C3H8).
1e.
Alkanols are stronger bases than water because they have a higher tendency to donate a proton (H+) to an acid. This is because the alkyl group in alkanols is electron-donating, which increases the electron density on the oxygen atom in the hydroxyl group (-OH).
1f. The major raw materials used in the Solvay process are
-salt (NaCl)
-limestone (CaCO3)
-ammonia (NH3).
1g. Geometric isomerism is a type of stereoisomerism that arises when two or more compounds have the same molecular formula and connectivity, but differ in the spatial arrangement of their atoms due to restricted rotation around a double bond or ring.
1h. Water gas is a better fuel than producer gas because it has a higher calorific value and a higher percentage of hydrogen gas.
1hi. Heat of combustion is the amount of heat energy released when one mole of a substance undergoes complete combustion with oxygen under standard conditions.
1ji. Faraday’s second law of electrolysis states that the amount of substance produced at an electrode during electrolysis is directly proportional to the quantity of electricity passed through the electrolyte. It can be expressed mathematically as:
m = (Q * M) / (n * F)
1jii. To calculate the amount of silver deposited, we can use Faraday’s law of electrolysis, which states that:
m = (Q * M) / (n * F)
Plugging in the values, we get:
m = (10920 C * 107.87 g/mol) / (1 * 96500 C/mol)
m = 12.17 g
Therefore, the amount of silver deposited when 10920 coulombs of electricity is passed through a solution of a silver salt is 12.17 grams.
Section B.
2a. (i) The balanced equation for the reaction is:
NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + 2H2O
(2aii) To calculate the concentration of the acid in mol dm^-3, we need to use the equation:
n = m/M
n NaOH = 4 g / 40 g mol^-1 = 0.1 mol
Since 8.0 cm³ of the acid was used to neutralize the sodium hydroxide, we can use the equation:
n acid = c × V
c = n acid / V
Substituting the values we know, we get:
c = 0.1 mol / 0.008 dm³ = 12.5 mol dm^-3
There fire the concentration of the acid in mol dm^-3 is 12.5 mol dm^-3.
2bi.
i.The postulate that gases consist of small, spherical particles in constant random motion.
ii.The postulate that gas particles have no attraction or repulsion for each other.
2bii)
The Kinetic theory of gases describes how gases behave, but it’s not entirely accurate for real gases. The theory assumes that gas particles are small and move randomly, and that they don’t attract or repel each other. However, real gases have more complex behavior, and their particles can be different sizes and shapes.
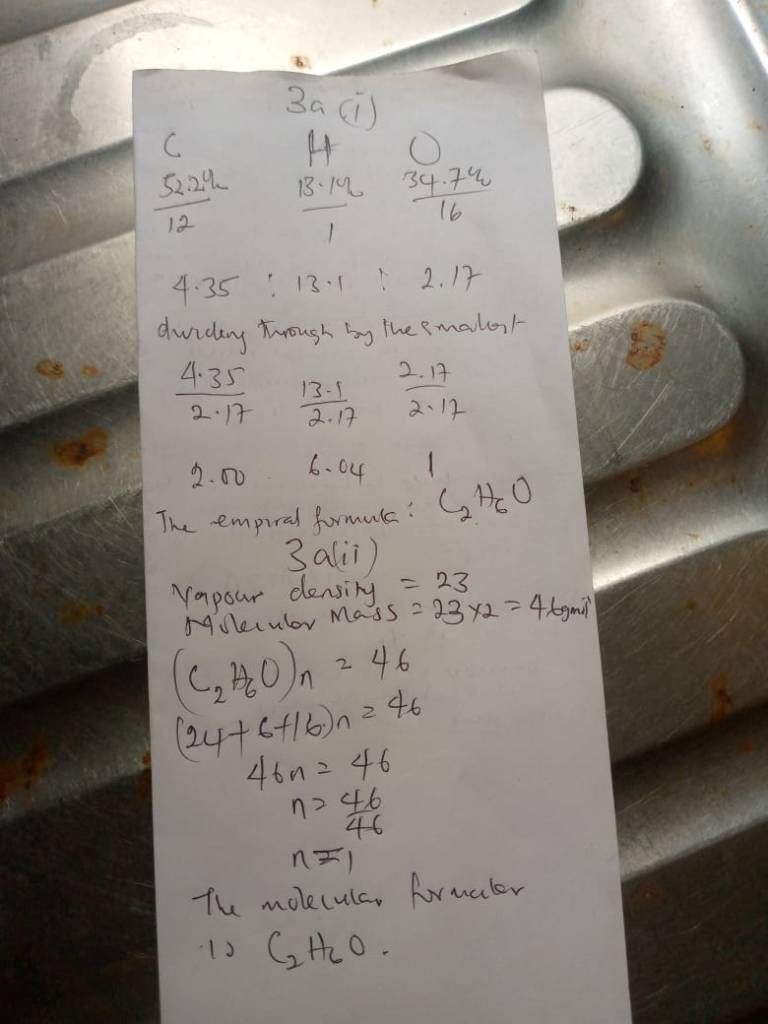
No 3
More loading….
Contact Us WhatsApp :- 08167972482

